39 the chemistry of baking
Chemistry of Cooking - Open Textbook Library The chemistry of cooking course seeks to understand the science behind our most popular meals by studying the behavior of atoms and molecules present in food. This book is intended to give students a basic understanding of the chemistry involved in cooking such as caramelization, Maillard reaction, acid-base reactions, catalysis, and fermentation. The Chemistry of Cake Ingredients - How Cakes Work | HowStuffWorks Liquids hydrate the protein, starch and leavening agents, allowing the chemical changes needed to develop the structure of the cake. Liquid vaporizes during the baking process, creating steam which expands the air cells and the volume of the cake. Liquids also help make the cake moist and improve its overall texture [source: Lauterbach ].
Decomposition of Sodium Bicarbonate - Balanced Equation Dec 12, 2019 · One way to speed up the decomposition of the dry ingredient is by heating it in a warm oven. Baking soda starts to break into washing soda, carbon dioxide, and water at room temperature when mixed with water, which is why you shouldn't store baking soda in an open container or wait too long between mixing a recipe and putting it in the oven.

The chemistry of baking
The chemistry of baking a biscuit - Chemwatch Baking involves a series of chemical reactions The glue (ten) keeping it together First things first: the dough. Very basic dough has two main ingredients—flour and water. There are a range of different kinds of flour and it's important to select the right type of flour for your recipe. Maillard reaction - Wikipedia The Maillard reaction (/ m aɪ ˈ j ɑːr / my-YAR; French: ) is a chemical reaction between amino acids and reducing sugars that gives browned food its distinctive flavor. Seared steaks, fried dumplings, cookies and other kinds of biscuits, breads, toasted marshmallows, and many other foods undergo this reaction. The Organic Chemistry of Baking Bread - Practically Science The Organic Chemistry of Baking Bread. The chemistry that underlies the browning of bread. meats, etc. was first defined in 1912 by Louis-Camille Maillard and involves the polymerization of sugars and proteins. While this reaction is obviously messy (i.e. has many different pathways), the dominant chemical mechanisms were identified in a ...
The chemistry of baking. Baking and Chemistry - American Chemical Society Baking and Chemistry Learning chemistry can be as easy as pie, or maybe just a piece of cake. Explore the chemistry of baking cookies, bread, pie, and cake, and investigate the science that's behind ingredients in your cupboard. Food Chemistry Cakes Cookies Powders Baked Goods ACS ChemClub Cookbook It's a cookbook! It's a chemistry book! It's both! The chemistry of baking powder | Resource | RSC Education 2H⁺ (aq) + CO₃²⁻ (aq) → H₂O (l) + CO₂ (g) for aqueous metal carbonates. Get your students engaged in a flash with this impressive demo. Try these ideas to help students better understand this scientific concept. Tips and resources to help you teach chemical processes and organic reaction mechanisms. Chemistry of Baking Fine ingredients, perfect chemistry, beautiful designs. My Story "As delicious as it is beautiful!" ... Don't Mix Baking Soda and Vinegar for Cleaning | Apartment ... Apr 05, 2021 · If you’re planning to use baking soda and vinegar together, Morris suggests using the mixture while it’s still bubbling – and ideally, directly on the surface you’re cleaning. For example, one useful method Morris suggests is to dump a bit of baking soda down a garbage disposal, followed by a couple glugs of vinegar.
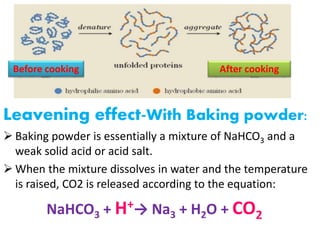
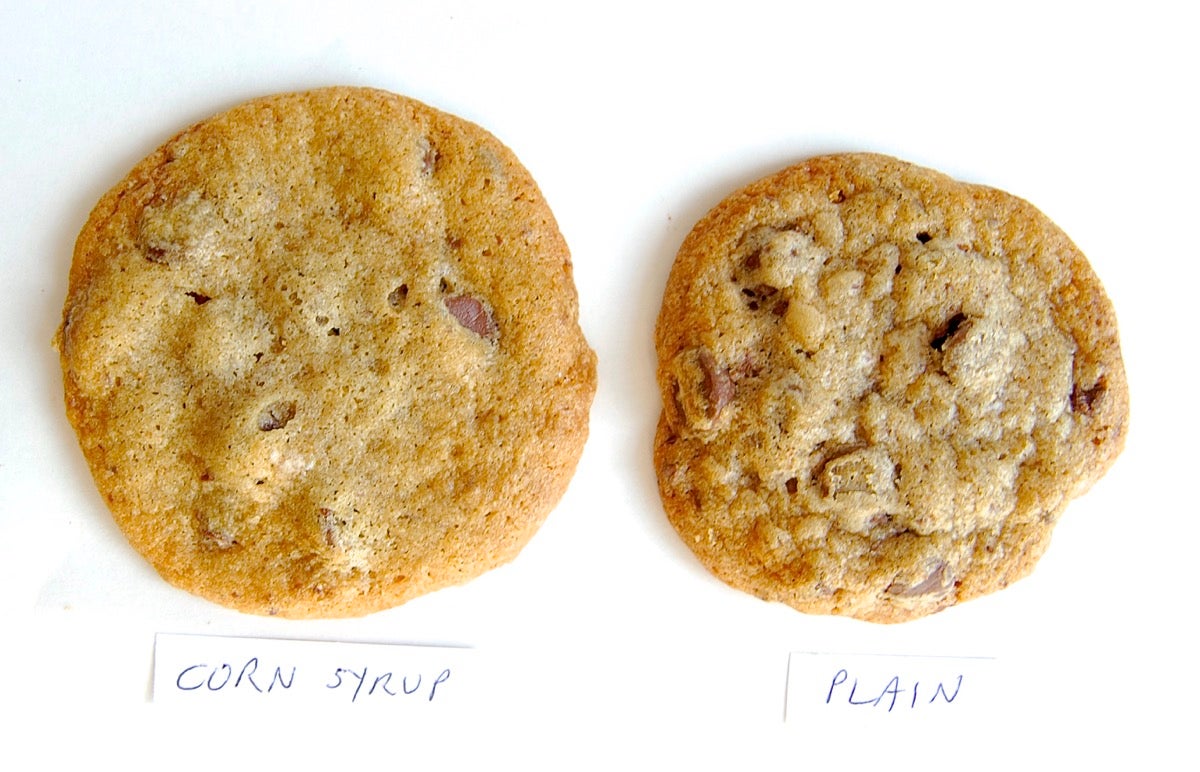
Chemistry of Breadmaking: An Introduction to the Science of Baking Chemistry of Breadmaking: An Introduction to the Science of Baking. Chemistry of Breadmaking: An Introduction to the Science of Baking. Watch on. 0:00 / 5:30. This video is intended to help people interested in chemistry learn something about baking, and those interested in baking learn a little bit about the science behind baking. Show More. The fundamental chemistry of baking cookies | 2020-04-10 | Snack Food ... Fundamental chemistry occurs when adding baking soda to the mixer. The sodium bicarbonate neutralizes the acidic ingredients (including high-fructose corn syrup, buttermilk, some flavors, etc.) producing carbon dioxide gas for cell formation. The Chemistry of Baking | PDF - Scribd Baking powder Baking powder is essentially a mixture of NaHCO3 and a weak solid acid or acid salt. When the mixture dissolves in water and the temperature is raised, CO2 is released according to the equation: NaHCO3 + H+ (from the acid) ! Na+ + H2O + CO2 The most common acids used are given in Table 1. The Science Behind Baking Ingredients - The Spruce Eats Commonly used baking fats include butter, shortening, coconut oil, and (less rarely these days) lard. Sugar Is Sweet and Helps Tenderize Sugar adds sweetness, as well as contributing to the product's browning. Sugar tenderizes a cake by preventing the gluten from forming. Sugar also holds moisture in the finished product.
About — Chemistry of Baking Over the years, I've practiced countless times & have added to the lessons my mom taught me. The name of my business comes from the combination of my love for chemistry (I have a B.S. in biochemistry) + my love for baking. I acquired both of these passions from my mom because she was also a baking chemist before she passed away. - The Chemistry of Cupcakes The baking powder helps the cupcake to form into its distinct shape. This reaction occurs when the cupcakes are in the oven baking. Chemistry's Role. Flour is created in a lab. Flour is made by grinding grains of wheat or other types alike it. Baking powder is also created in a lab. Baking powder is made by adding bicarbonate to a weak acid. Chemistry is a Piece of Cake—The Science of Baking Many chemical reactions are involved in the baking of cakes and pastries. The sulfur in gluten proteins form disulfide bonds, giving dough its elasticity. Water dissolves the other components while distributing the heat evenly when the pastry is cooking in the oven. Yeast ferments the sugars, creating gas that expands the dough. The Chemistry of Baking Cookies - ThoughtCo Chemistry During Baking If the ingredients are high quality, measured carefully, and mixed as they should be, chemical magic happens in the oven to make great cookies. Heating sodium bicarbonate causes it to decompose into water and carbon dioxide : 2NaHCO 3 → Na 2 CO 3 + H 2 O + CO 2
Baking Bread: The Chemistry of Bread-Making - Compound Interest The process of making bread can be broken down at a very simple level into four steps. First, the ingredients are mixed; the four basic ingredients used to make a bread are flour, water, yeast, and salt. Combining these creates a dough, which is then kneaded before being left to rise, before being baked. Sounds pretty straightforward, right?
The chemistry of cake baking - Sciencenorway.no Wheat flour is comprised of starchy grain covered in proteins. Gluten is the name of the substance created when the proteins in the flour get moist. When water is added, the proteins glutenin and gliadin absorb the liquid, stretching out and getting sticky. The more you knead the dough, the more gluten you get.
The chemistry of cookies - Stephanie Warren | TED-Ed You stick cookie dough into an oven, and magically, you get a plate of warm, gooey cookies. Except it's not magic; it's science. Stephanie Warren explains via basic chemistry principles how the dough spreads out, at what temperature we can kill salmonella, and why that intoxicating smell wafting from your oven indicates that the cookies are ready for eating.
Chemical Change Definition in Chemistry - ThoughtCo Jan 13, 2020 · Learn the definition of a chemical change as the term is used in chemistry and discover examples of chemical changes. ... Combining baking soda and vinegar is an ...
Turn Baking Soda Into Washing Soda - ThoughtCo Jan 09, 2020 · Sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) and sodium carbonate (washing soda) are similar molecules. The difference is how much water is incorporated into the molecule. If you bake baking soda, it decomposes to form washing soda, releasing carbon dioxide and water. Over time, washing soda decomposes to form sodium oxide, releasing carbon dioxide.
[PDF] THE CHEMISTRY OF BAKING | Semantic Scholar For bread baking, the flour should be a wheat flour which is high in gluten (protein) as this is the substance that gives bread its fine texture and supports the ingredients during rising. Yeast Yeast is a plant that feeds on starch and sugars, releasing CO2, alcohol and sugar. The CO2 bubbles give the dough a light, airy texture.
The Chemistry of Baking - News-Medical.net The chemistry of cookies - Stephanie Warren Baking at the Micro Biotic Level The yeast Saccharomyces Cerevisiae, characteristically known as baker's yeast, is what humans have used in the fermentation of many consumables for thousands of years.
NIST Chemistry WebBook A Guide to the NIST Chemistry WebBook: A guide to this site and the data available from it. Gas-Phase Ion Thermochemistry: An in-depth explanation of gas phase ion data available from this site. NIST Organic Thermochemistry Archive: A description of the primary source of thermochemical data for this site.
Science in Action: The Chemistry of Baking - YouTube Science in Action: The Chemistry of Baking 6,391 views Premiered Sep 7, 2020 132 Dislike Share Save Museum of Science, Boston 25.5K subscribers Join Museum of Science educators as they demonstrate...
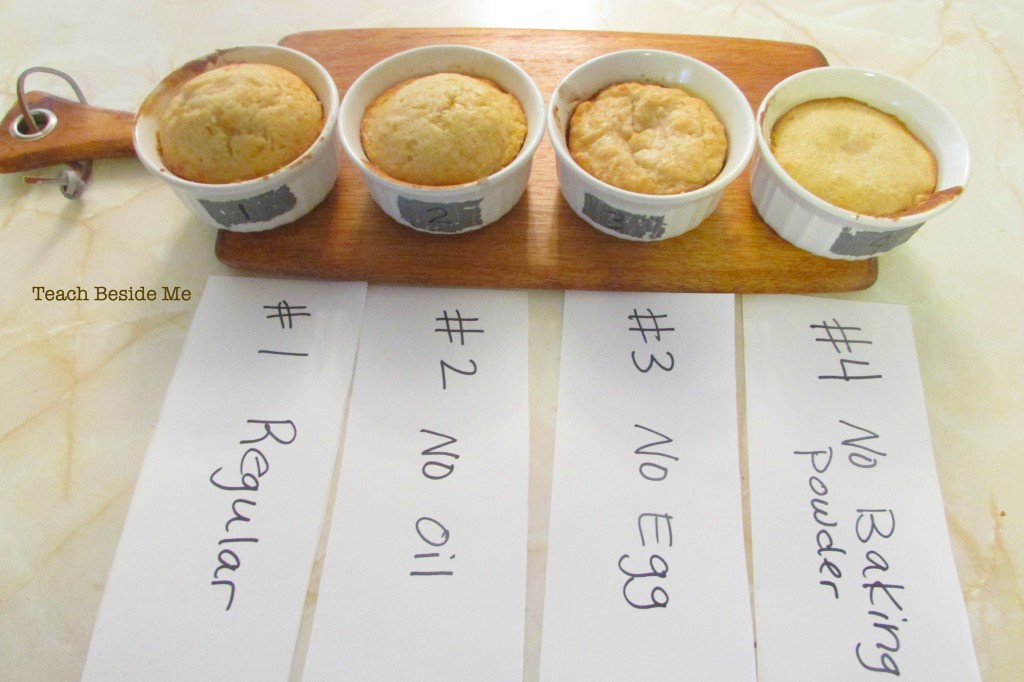
Chemistry of Baking Ingredients 1: How Much Baking Powder Do Quick ... One of the products of this chemical reaction is carbon dioxide gas, which provides the leavening for the baked product. As the batter is baked, the carbon dioxide produced by the baking powder makes bubbles in the batter. The bubbles are trapped by the surrounding structure of the batter, mainly supported by proteins in the flour and eggs.
The Chemistry of Baking - University of South Carolina The processes of cooking and baking can be described by molecular-level chemical reactions. By identifying the key variables of flour-based baked goods, it is possible to manipulate recipes and create an improved overall final product. This thesis explores the effects of manipulating proteins, water, lipids, air, and the biochemical
Chemist Solutions: The Science of Baking on Chemistry Cachet One of the absolute COOLEST things about chemistry is baking! Baking is a very delicate, intricate since that allows for so many amazing foods to turn out so different. Like cakes and cookies! Most of them have almost the exact same list of ingredients, but depending on the amounts and how you put it together: it can turn out completely different.
PDF THE CHEMISTRY OF BREAD-MAKING - Compound Interest THE CHEMISTRY OF BREAD-MAKING Baking bread may seem like a very simple process. It's a combination of only four different ingredients: flour, water, yeast, and salt. However, there's a lot of science in how these four ingredients interact, and how varying them varies the bread's characteristics.
Culinary Science aka Kitchen Chemistry - The Homeschool Scientist If you cook or bake, you like or know something about kitchen chemistry. In any baking recipe, every ingredient has a purpose. For example, in a cake, flour gives the structure, eggs bind the ingredients, baking powder and baking soda make it rise, fats like butter and oil make it less chewy, and sugar sweetens and keeps it moist. Amazing! Right?
The chemistry of cookies - Stephanie Warren - YouTube Stephanie Warren explains via basic chemistry principles how the dough spreads out, at what temperature we can kill salmonella, and why that intoxicating smell wafting from your oven indicates that...
The Organic Chemistry of Baking Bread - Practically Science The Organic Chemistry of Baking Bread. The chemistry that underlies the browning of bread. meats, etc. was first defined in 1912 by Louis-Camille Maillard and involves the polymerization of sugars and proteins. While this reaction is obviously messy (i.e. has many different pathways), the dominant chemical mechanisms were identified in a ...
Maillard reaction - Wikipedia The Maillard reaction (/ m aɪ ˈ j ɑːr / my-YAR; French: ) is a chemical reaction between amino acids and reducing sugars that gives browned food its distinctive flavor. Seared steaks, fried dumplings, cookies and other kinds of biscuits, breads, toasted marshmallows, and many other foods undergo this reaction.
The chemistry of baking a biscuit - Chemwatch Baking involves a series of chemical reactions The glue (ten) keeping it together First things first: the dough. Very basic dough has two main ingredients—flour and water. There are a range of different kinds of flour and it's important to select the right type of flour for your recipe.

![PDF] THE CHEMISTRY OF BAKING | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/3eabd1e38cdaa8992e6d3693653081352a753ec0/7-Figure1-1.png)























/chocolate-chip-cookies-104629801-5921de853df78cf5fa84a9be.jpg)







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TC_607372-substitute-baking-powder-and-baking-soda-5abaaa97ba617700376d9fde.png)
0 Response to "39 the chemistry of baking"
Post a Comment