40 Surface Tension Intermolecular Forces
PDF Microsoft PowerPoint - Chapter 11 - Intermolecular Forces, Liquids... Determining Intermolecular Forces. • All chemicals exhibit dispersion forces. • When the shapes of two substances have comparable molar masses and. • Surface tension results from the net inward force experienced by the molecules on the surface of a liquid. • It causes water to "bead up" when in... Surface Tension | Adhesive Forces Surface Tension. Surface tension is measured as the energy required to increase the surface area of a liquid by a unit of area. The surface tension of a liquid results from an imbalance of intermolecular attractive forces, the cohesive forces between molecules
4.1 Intermolecular and interatomic forces | Intermolecular... | Siyavula Intermolecular forces are one of the main reason that matter exists in different states (solids, liquids and gases). In this experiment learners will investigate how intermolecular forces affect evaporation, surface tension, solubility, boiling points and capillarity.

Surface tension intermolecular forces
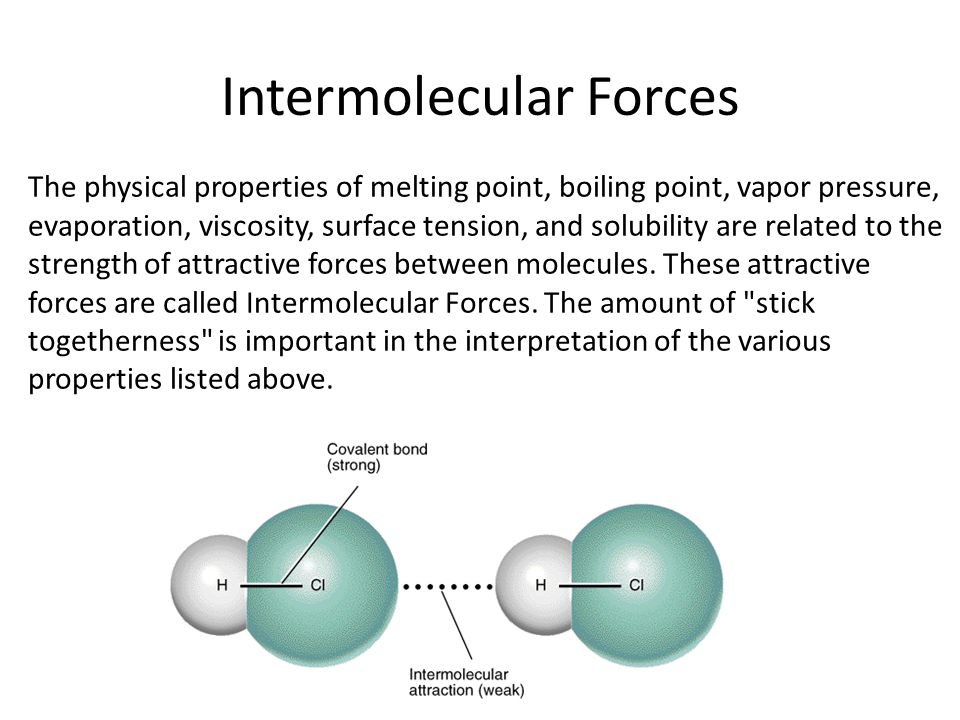
Intermolecular Forces | Surface Tension Intermolecular forces (IMF) are the forces which cause real gases to deviate from ideal gas behavior. They are also responsible for the formation of the This works to reduce the surface area, attempting to create the shape with the minimal surface area, a sphere. The surface tension is the amount of... PDF Surface Tension Because surface tension causes the liquid surface to contract, a force F is needed to move the slider to the right and extend the surface. We have seen that surface tension arises because of the intermolecular forces of attraction that molecules in a liquid exert on one another. Surface Tension: Intermolecular forces Surface Tension: Intermolecular forces. The force between the like molecules which holds the liquid together is called 'cohesive force'. Different liquids do not mix together due to their physical properties such as density, surface tension force, etc. For example, water and kerosene do not mix...
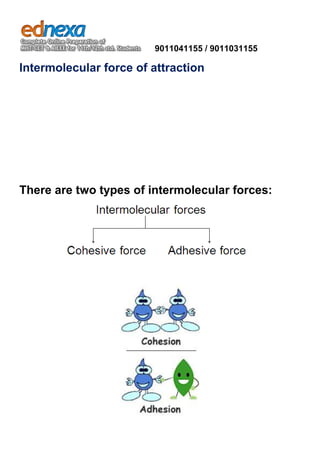
Surface tension intermolecular forces. Chemistry: The Effects of Intermolecular Forces Surface tension: Liquids with stronger intermolecular forces tend to have higher surface tension than those with weak intermolecular forces. For example, if you pour a very small amount of water on a table, it will tend to collect together in one large drop. On the other hand... Surface tension [Molecules in liquids experience strong intermolecular attractive forces. When those forces act between like molecules, they are referred to as Detergents lower the surface tension of water. Detergent molecules have two ends, one hydrophobic end, repelled by water and one hydrophilic... Surface tension - Wikipedia Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows heavier than water i.e... Types of Intermolecular Force of Attraction and Molecular... | Kullabs There are two types of intermolecular forces. They are Cohesive Force Adhesive Force Cohesive Force The inter-molecular force of attraction that The surface tension of a liquid is measured as the force per unit length of an imaginary line drawn on the free surface, perpendicular to it at every point...
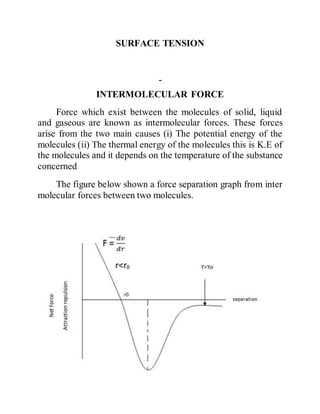
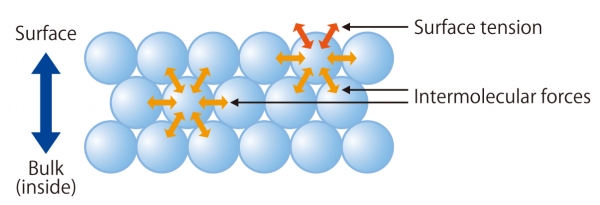
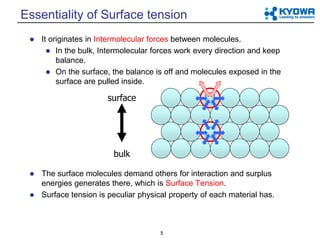
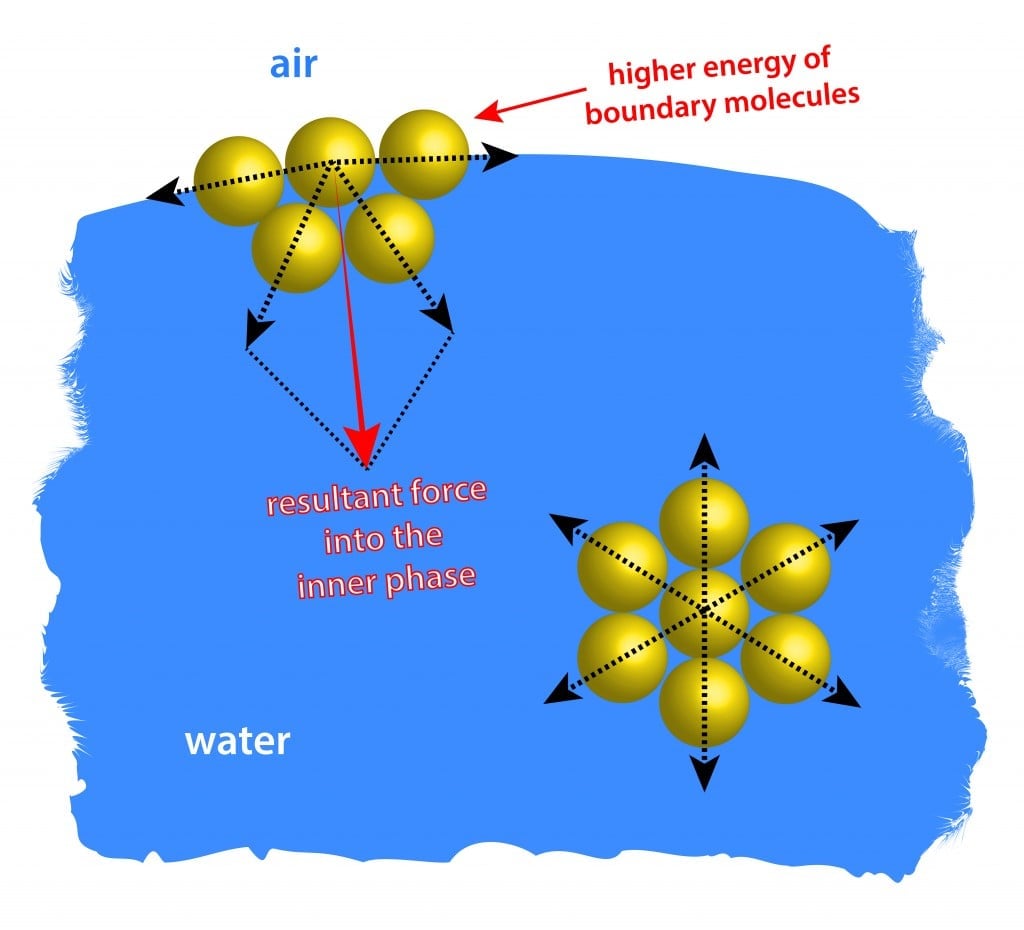
Surface Tension Surface tension is caused by the effects of intermolecular forces at the interface. In general, surface tension decreases when temperature increases because cohesive forces decrease with an increase of molecular thermal activity. PDF Estimation of surface tension based on intermolecular forces Physical origin of surface tension/surface energy. • "Unhappy" molecules at the surface: they are missing half their attractive interactions. Relationship of surface tension with other material properties Derivation of surface tension theoretically from knowledge of intermolecular forces. PDF chapter_11au | Intermolecular Forces Affect Many Physical Properties Intermolecular Forces. The attractions between molecules are not nearly as strong as the intramolecular attractions that hold compounds together. Surface tension results from the net inward force experienced by the molecules on the surface of a liquid. Intermolecular Forces. How is the surface tension related to the intermolecular forces? As a general rule, stronger intermolecular forces result in higher surface tension. A good example is water, where there are strong dipole intermolecular forces and has high surface tension. Liquids with lower intermolecular forces like oils have a resulting lower surface tension.
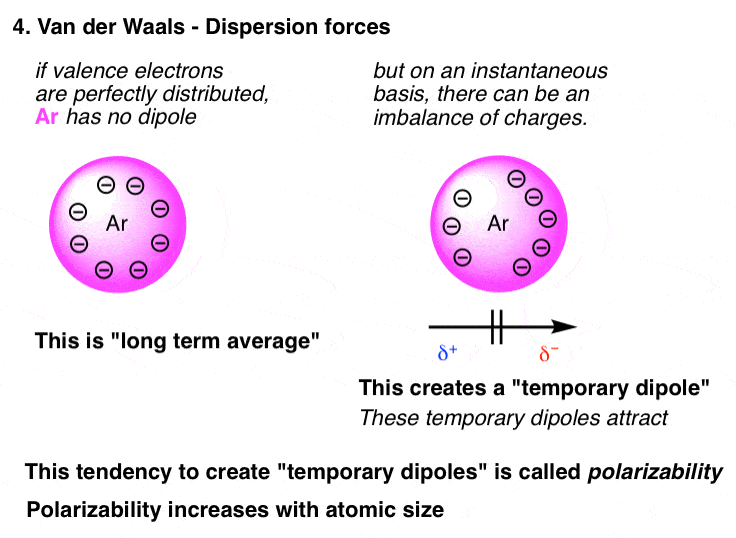
[PDF] Intermolecular and surface forces | Semantic Scholar Strong Intermolecular Forces: Covalent and Coulomb Interactions. Interactions Involving Polar Molecules. Interactions Involving the Polarization of Molecules. van der Waals Forces. Repulsive Forces, Total Intermolecular Pair Potentials, and Liquid Structure. (PDF) INTERMOLECULAR AND SURFACE FORCES... - Academia.edu Intermolecular Force-Laws and Interaction Potentials: Long- and Short-Range Forces 9 1.7. First Successful Phenomenological Theories 12 1.8. 2D Structures on Surfaces: Soluble and Insoluble Monolayers 520 Contents xv 19.10. Line Tension and 2D Micelles (Domains) 521 19.11. What Is Surface Tension? Definition and Experiments Causes of Surface Tension. Various intermolecular forces, such as Van der Waals forces, draw the liquid particles together. Surface tension (denoted with the Greek variable gamma) is defined as the ratio of the surface force F to the length d along which the force acts Surface tension Surface tension. Surface tension is also related to the intermolecular forces in the liquid. The molecules in liquids are held closely and hence attract each other. A molecule in the bulk of the liquid is attracted equally on all sides so that the net attractive pull on the molecule is zero.
Surface tension - New World Encyclopedia In physics, surface tension is an effect within the surface layer of a liquid that causes that layer to behave as an elastic sheet. This effect allows insects (such as the water strider) to walk on water. It allows small metal objects such as needles, razor blades...
Surface Tension | Chemistry for Non-Majors Surface Tension. Molecules within a liquid are pulled equally in all directions by intermolecular forces. However, molecules at the surface are pulled downwards and sideways by other liquid molecules, but not upwards away from the surface.
11.4: Intermolecular Forces in Action- Surface Tension, Viscosity... Surface tension is the energy required to increase the surface area of a liquid by a unit amount and varies greatly from liquid to liquid based on the nature of the intermolecular forces, e.g., water with hydrogen bonds has a surface tension of 7.29 x 10-2 J/m2 (at 20°C), while mercury with metallic...
Surface Tension Cohesion and Surface Tension. The cohesive forces between molecules down into a liquid are shared with all neighboring atoms. Molecules in the liquid state experience strong intermolecular attractive forces. When those forces are between like molecules, they are referred to as cohesive...
Intermolecular Force - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Intermolecular forces are weak relative to intramolecular interactions (also called intramolecular forces) which are the interactions (forces) that hold a Although the shape of a molecule has a large bearing on the phases it forms and the temperatures at which it transforms, other considerations, such...
Surface tension (video) | Khan Academy Surface tension in water, and how the surface tension is related to hydrogen bonding. And this is what allows them to actually have a stronger, I guess you could say, intermolecular force at the surface than you have within the body, and that causes a phenomenon known as surface tension.
Surface and interfacial tension The surface tension, γ, may be defined as the force/unit length parallel to the surface which is exerted perpendicular to any line drawn in the surface. A further contribution was made by Fowkes who assumed that the contributions made by different types of intermolecular interaction are additive and...
Intermolecular forces surface tension - Big Chemical Encyclopedia Manifestations of Intermolecular Forces Surface tension—the tendency for liquids to minimize their surface area—is a direct result of intermolecular forces. Both surface tension and viscosity increase with greater intermolecular forces.
Intermolecular Forces and Surface Tension The stronger the intermolecular forces acting between the particles in a liquid, the stronger the cohesive forces, the greater the surface tension of the liquid. If you wanted to float a steel needle on the surface of these liquids, as we did in the first section...
INTERMOLECULAR FORCES-SURFACE TENSION - YouTube A discussion and demonstration of intermolecular forces, with examples of surface tension.
Surface and Interfacial Tension - Nanoscience Instruments 1 - intermolecular forces between molecules in the bulk and the interface. How is surface and interfacial tension measured? In force tensiometry the force experienced by a probe at the liquid surface is directly measured. With the Attension Sigma tensiometers, three techniques are available...
Measuring Surface Tension to Investigate Intermolecular Forces Considering the foundational role intermolecular forces (IMFs) have when trying to explain and understand chemical phenomena, it is likely that The knowledge developed from this entire activity stems from an investigation of one property—surface tension. Though I have certainly paid lip...
Surface Tension: Intermolecular forces Surface Tension: Intermolecular forces. The force between the like molecules which holds the liquid together is called 'cohesive force'. Different liquids do not mix together due to their physical properties such as density, surface tension force, etc. For example, water and kerosene do not mix...
PDF Surface Tension Because surface tension causes the liquid surface to contract, a force F is needed to move the slider to the right and extend the surface. We have seen that surface tension arises because of the intermolecular forces of attraction that molecules in a liquid exert on one another.
Intermolecular Forces | Surface Tension Intermolecular forces (IMF) are the forces which cause real gases to deviate from ideal gas behavior. They are also responsible for the formation of the This works to reduce the surface area, attempting to create the shape with the minimal surface area, a sphere. The surface tension is the amount of...






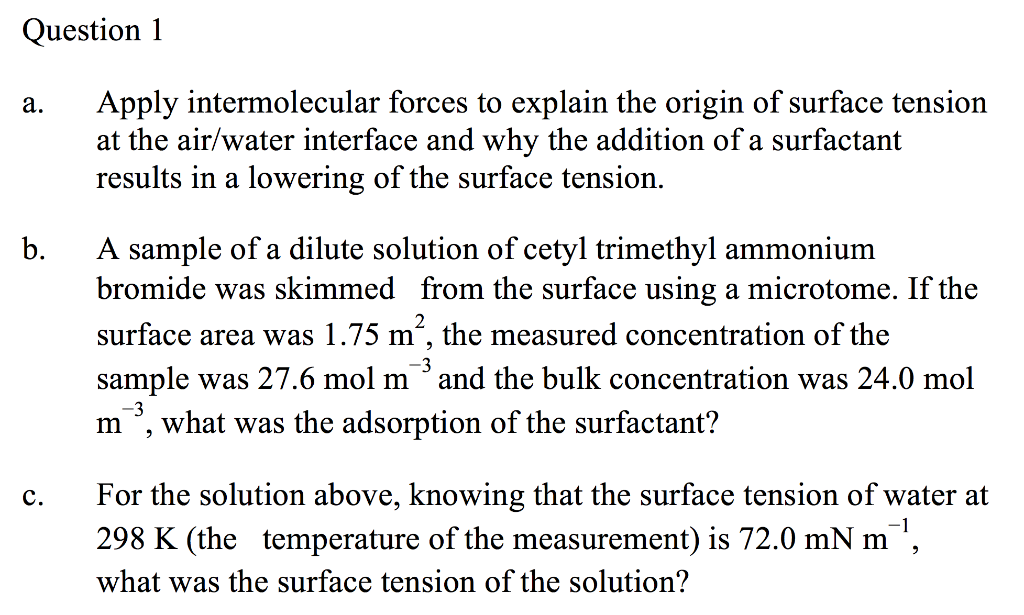


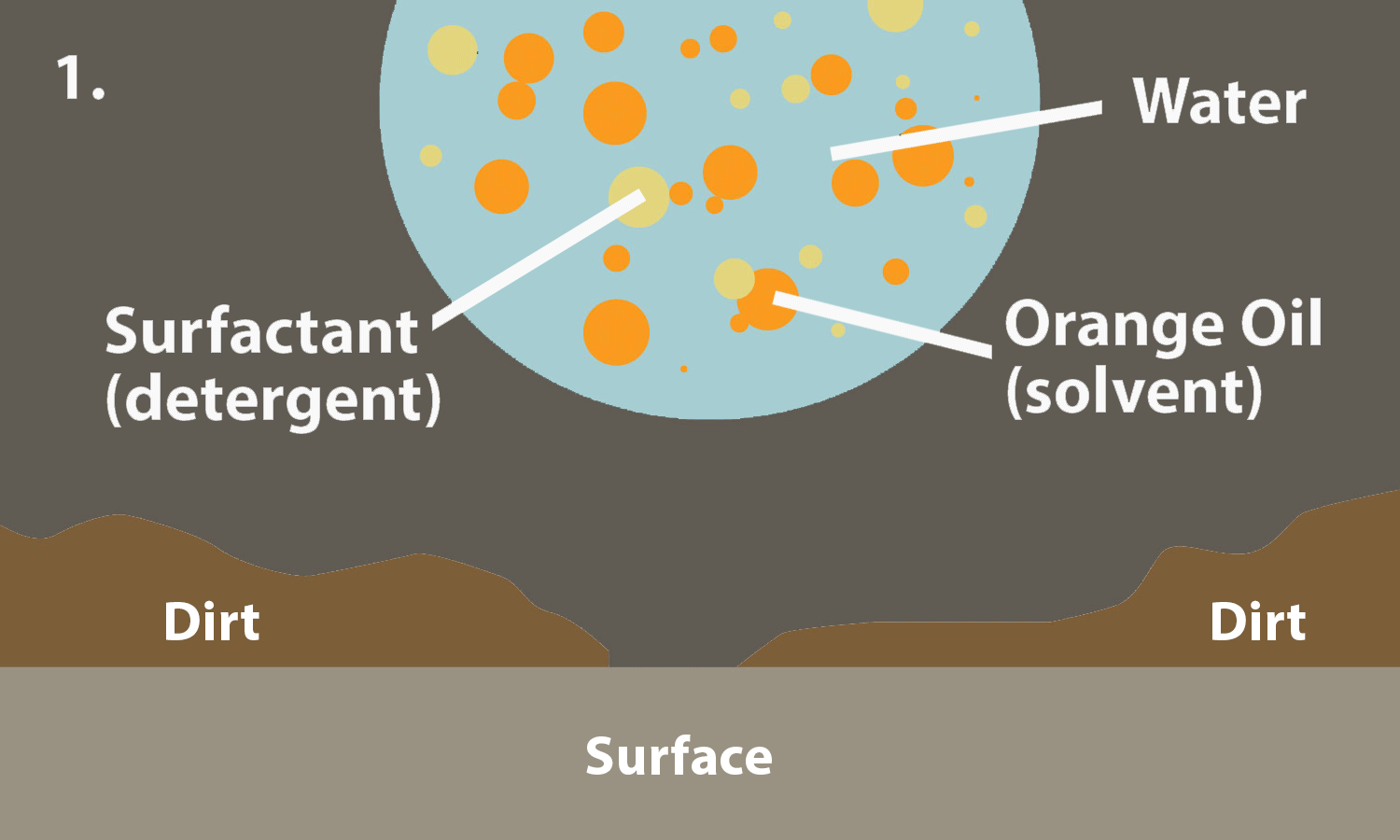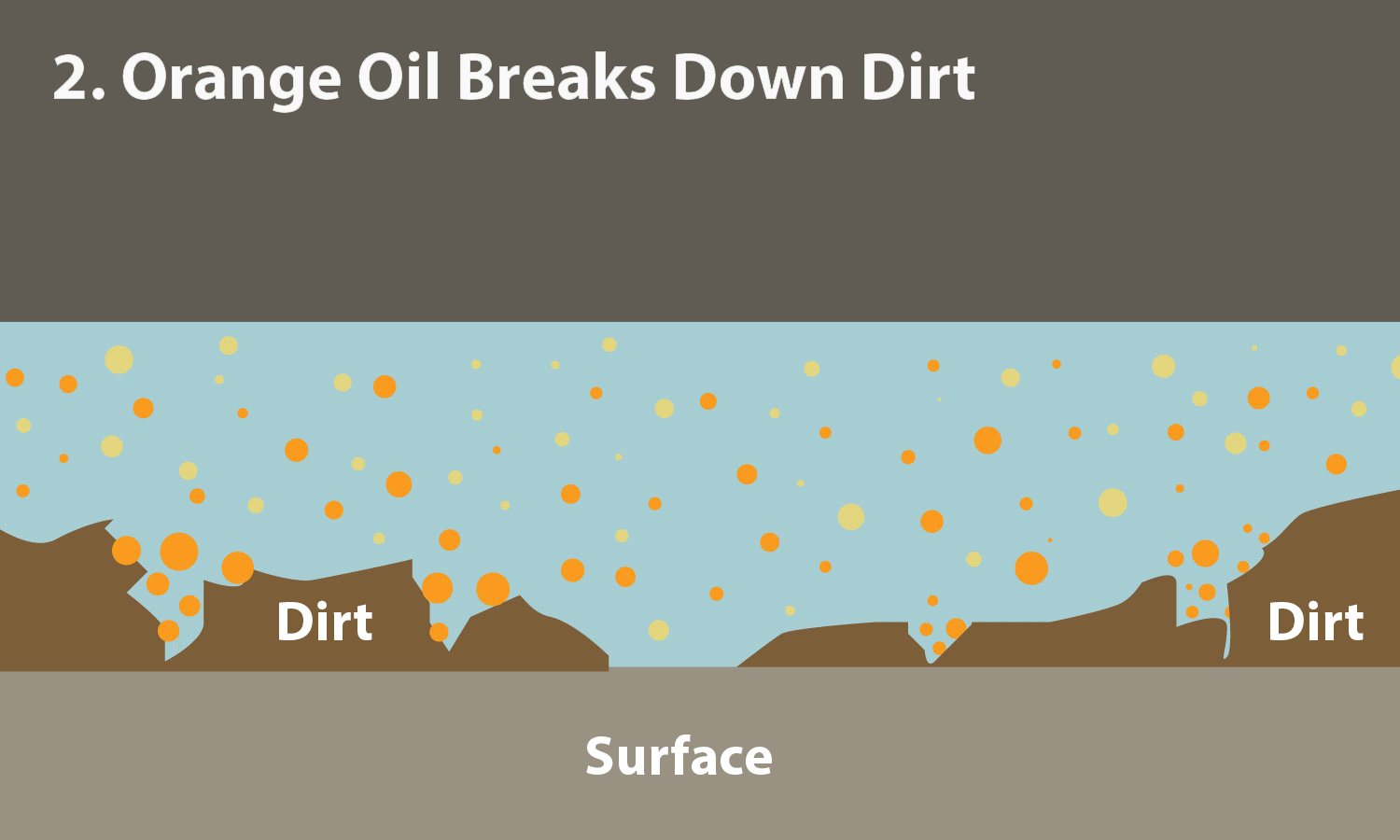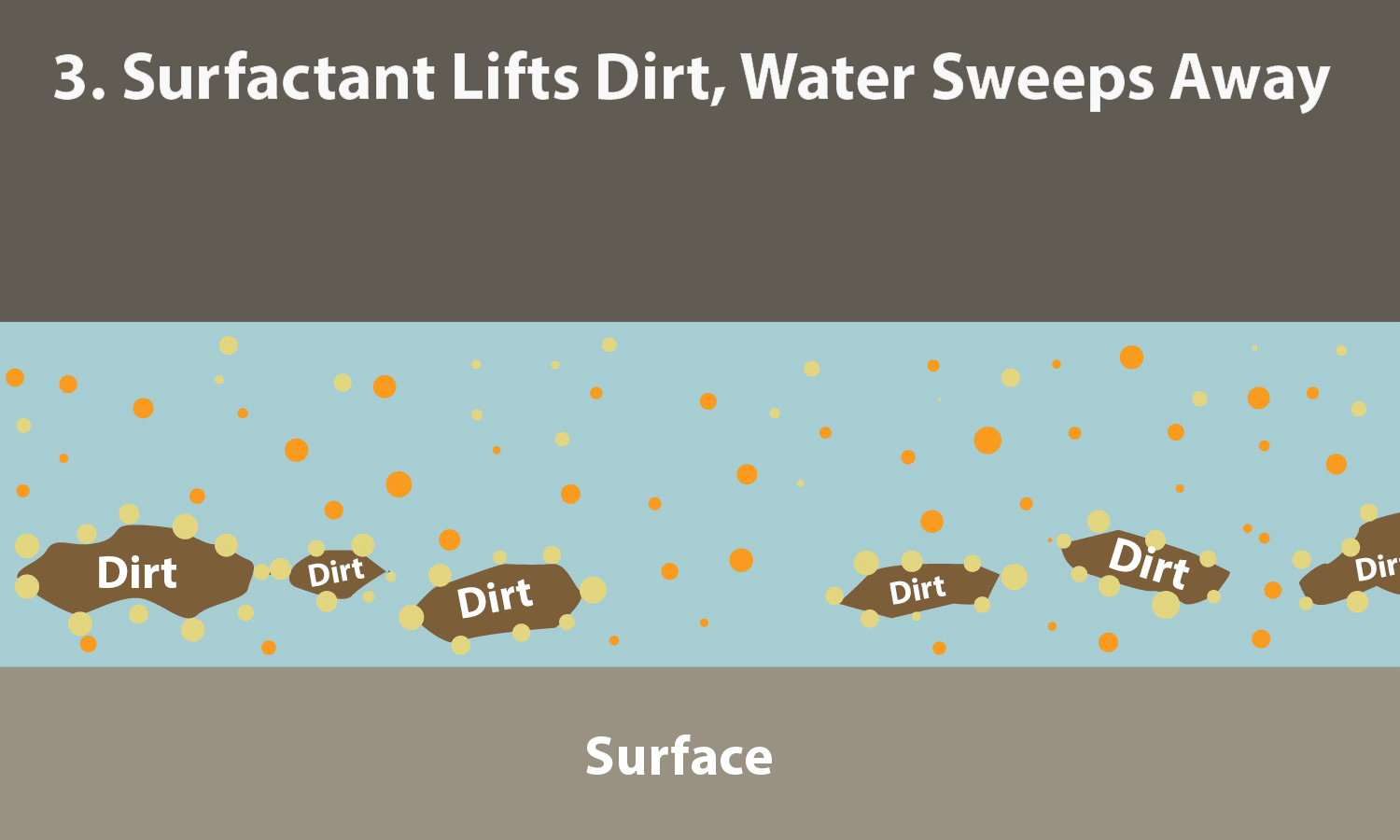














0 Response to "40 Surface Tension Intermolecular Forces"
Post a Comment