42 higher frequency hearing loss
High-Frequency Hearing Loss One of the most common types of hearing loss is high-frequency. This means that sounds at higher pitches are harder to hear, and it can affect anyone from any age group but becomes more prevalent in older adults or those who have been exposed to loud noise on a regular basis for an extended period. A high-frequency hearing loss is a hearing loss where you are unable to hear sounds that occur in the higher end of frequencies, which are frequencies of 2,000 Hz or higher. These sounds are also called the higher sounds or high-pitched sounds. A certain type of high-frequency hearing loss is called a ski-slope hearing loss, as it has the shape ...
High-Frequency Hearing Loss Symptoms and Causes. High-frequency hearing loss is going to have an effect on someone's capacity to have an understanding of speech. No matter how old you are, having high-frequency loss may affect your overall health, generating stress and anxiety, major depression and also societal seclusion.
Higher frequency hearing loss
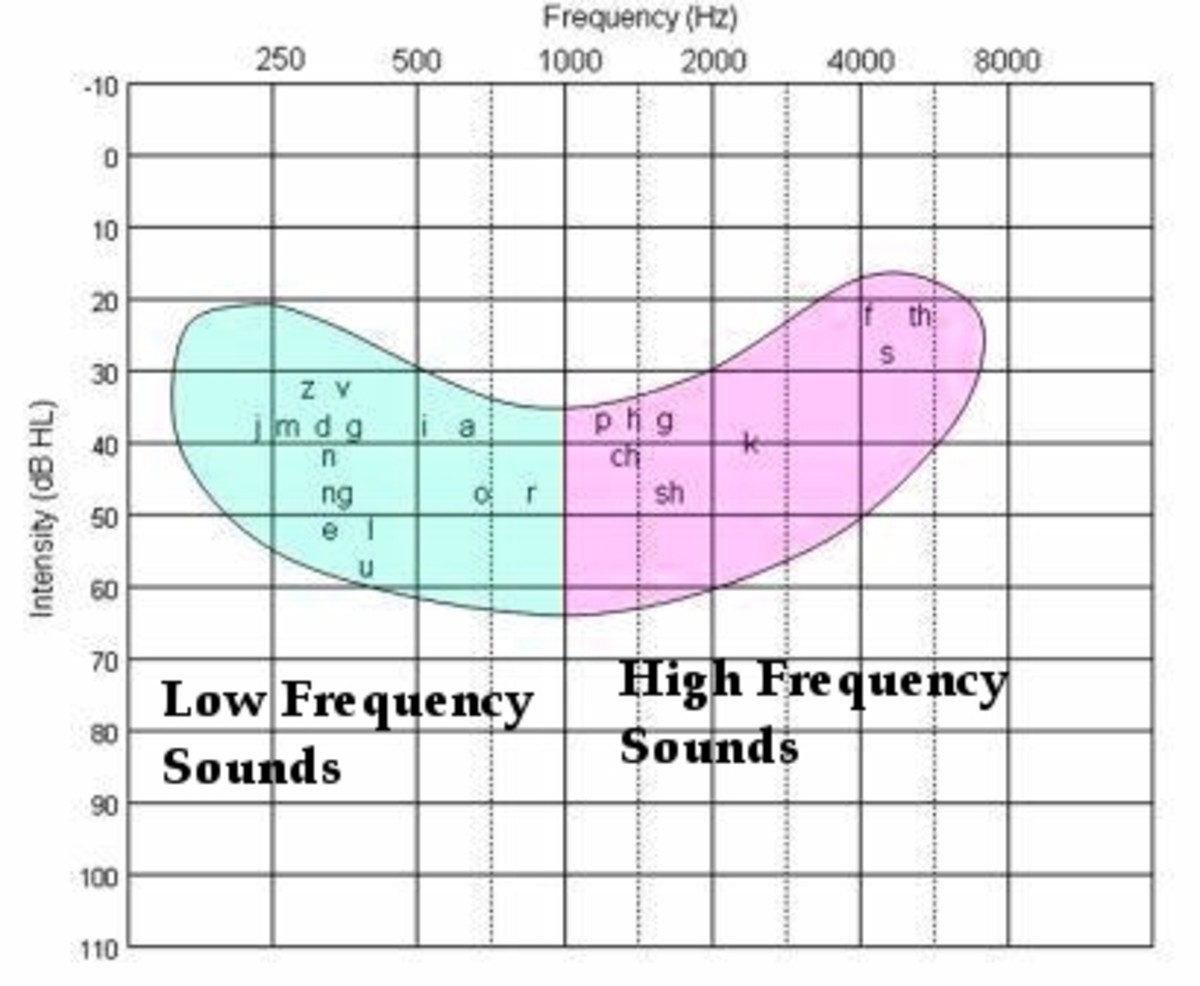
What is High Frequency Hearing Loss? High frequency hearing loss refers to having trouble hearing sounds in the 2,000 to 8,000 Hertz (Hz) range. This happens when sensory hearing cells within your ear's cochlea are damaged or die. These hair cells are charged with creating electrical impulses from the sounds that are collected by your ears. Neural- downsloping high-frequency hearing loss with a disproportionate loss of speech perception - degeneration of spiral ganglion cells Strial/metabolic- a flat SNHL with preserved speech perception - degeneration of stria vascularis Cochlear conductive- progressive downsloping high-frequency SNHL - increased stiffness of the basilar membrane People with high-frequency hearing loss tend to have difficulty hearing certain consonants, like s, h and f. This is because consonants are uttered at a higher frequency than vowels sounds. This can result in speech sounding muffled, especially when talking on the phone, watching TV or trying to have a conversation in background noise.
Higher frequency hearing loss. Moreover, the hearing loss demonstrated in the studies relating it to dementia is typically pronounced at high frequencies, which is consistent with age-related deterioration in the cochlea rather than damage to the central pathways caused by AD. Hearing professionals define high-frequency hearing loss as hearing loss that occurs between 2000 Hertz (Hz) - 8000 Hertz. Decreased hearing acuity in the high-frequency range is often the first sign of hearing loss. Following your hearing test, your hearing professional will explain your test results using an audiogram. High frequency hearing loss causes problems with hearing high-pitched sounds. It can also lead to problems understanding fast speech. Damage to the hair-like structures in your inner ear can cause... High-frequency hearing loss is one of the most common types of hearing loss. If it occurs to someone, they will find it difficult to hear high-pitched sounds. Even though anyone can get affected by it at any age, it is mainly seen among older adults facing age-related hearing loss problems. It is a type of sensorineural hearing loss.
What is High Frequency Hearing Loss? "High-frequency hearing loss means that high-pitched sounds are harder to hear," Shannon Basham, AuD, senior director of audiology and education at Phonak in... A high-frequency hearing loss will affect a person's ability to understand speech. This happens because the consonants (s, h, f) are high-frequency sounds that range from 1,500 to 6,000 Hertz. Losing hearing in those frequencies means that those sounds are harder to discern. For children, this can mean a negative impact on their education due to the inability to understand speech in the classroom.2 10 Reviews: Best Hearing Aid for High Frequency Loss (Jan 2022) High-pitched speech sounds are no longer a problem. by A. Wahyu · updated on Jan 05, 2022 · price $1,526.00 - $3,015.00 · 246 views · 7 visitors liked products on this page We hope you love the shops and products we recommend! Just so you know, our site may collect a share of sales or other compensation from the links on this ... "If you live long enough, you're going to suffer some hearing loss — it's part of the normal aging process," says Sean McMenomey, M.D., a professor of otolaryngology, head and neck surgery and neurological surgery at the New York University Langone Medical Center. One study, published in the March 1, 2017, issue of JAMA Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, found that while hearing ...
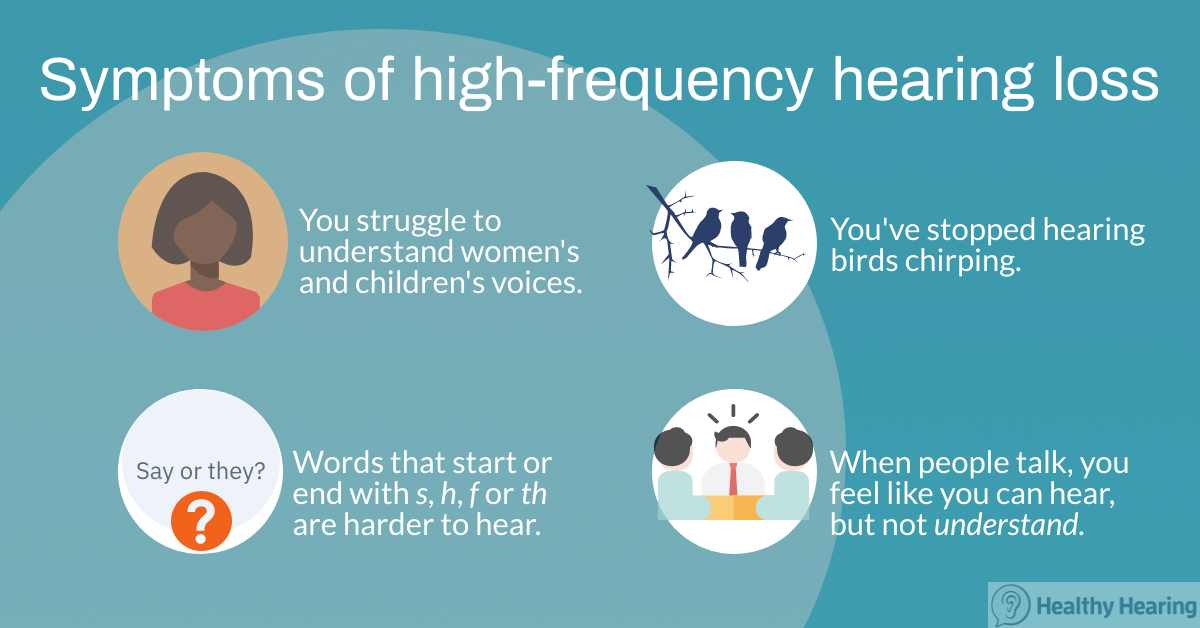
What is High-Frequency Hearing Loss? High frequency sensorineural hearing loss is a form of hearing impairment that can affect one ear or both ears. Sufferers of high tone hearing loss are unable to hear high-pitched sounds, however, they can still hear lower frequency sounds. High frequency hearing loss is one of the most common types of hearing loss. Although it can affect people of any age, it is more common in older adults and people exposed regularly to loud noises. Specifically sounds in the frequency range of approximately 2,000 Hertz (Hz) and 8,000 Hz become difficult to hear. What is high frequency hearing loss? To put it simply, a high frequency hearing loss means you are unable to hear sounds that are between 2,000 and 8,000 Hz. Hearing and understanding women's voices, children's voices and s, h or f sounds, for instance, is near impossible or inaudible. Even with the right amplification, people with high-frequency hearing loss may have trouble interpreting sounds, particularly speech. Those who suffer from low-frequency hearing loss, however, are better able to decode sounds once they are amplified when you wear hearing aids.
High-frequency hearing loss occurs when the tiny hair-like sensory hearing cells in your cochlea (inner ear) are damaged. These hair cells, known as stereocilia, are responsible for translating the sounds your ears collect into electrical impulses, which your brain eventually interprets as recognizable sound. Causes of high-frequency hearing loss
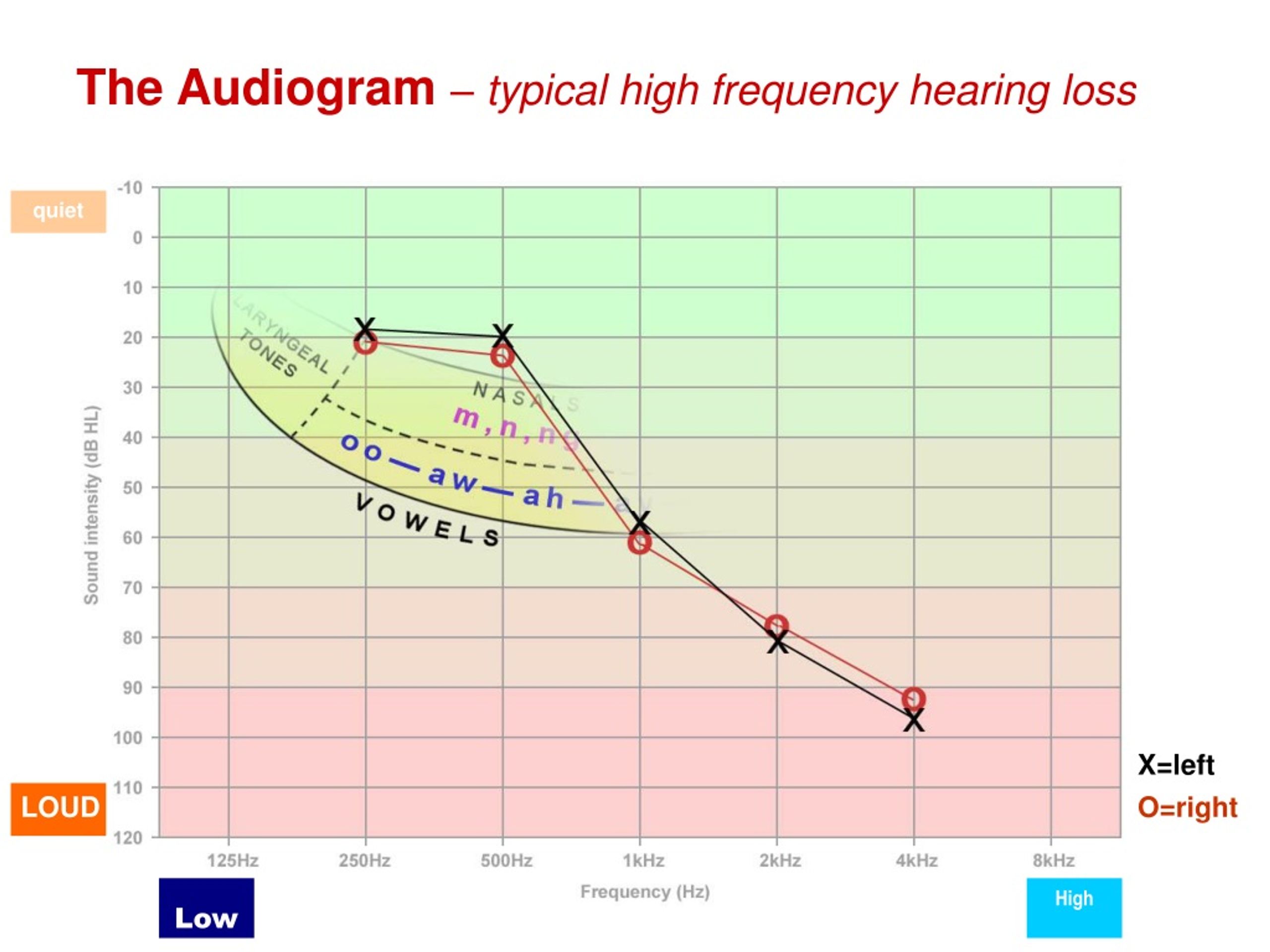
Hearing professionals define high-frequency hearing loss as hearing loss that occurs between 2000 Hertz (Hz) – 8000 Hertz. Decreased hearing acuity in the high-frequency range is often the first sign of hearing loss. Following your hearing test, your hearing professional will explain your test results using an audiogram.

Newcastle Upon Tyne's Tallest Building, Old & New Architecture, Hadrian Tower, Newcastle Upon Tyne, Tyne & Wear, England.
High-frequency hearing loss can be caused by a variety of reasons. These include noise, aging, genetics, and disease. Menieres disease affects the inner ear and often happens to people between the ages of 30 and 50 years old. This can cause tinnitus, vertigo, hearing loss, and intense episodic dizziness.
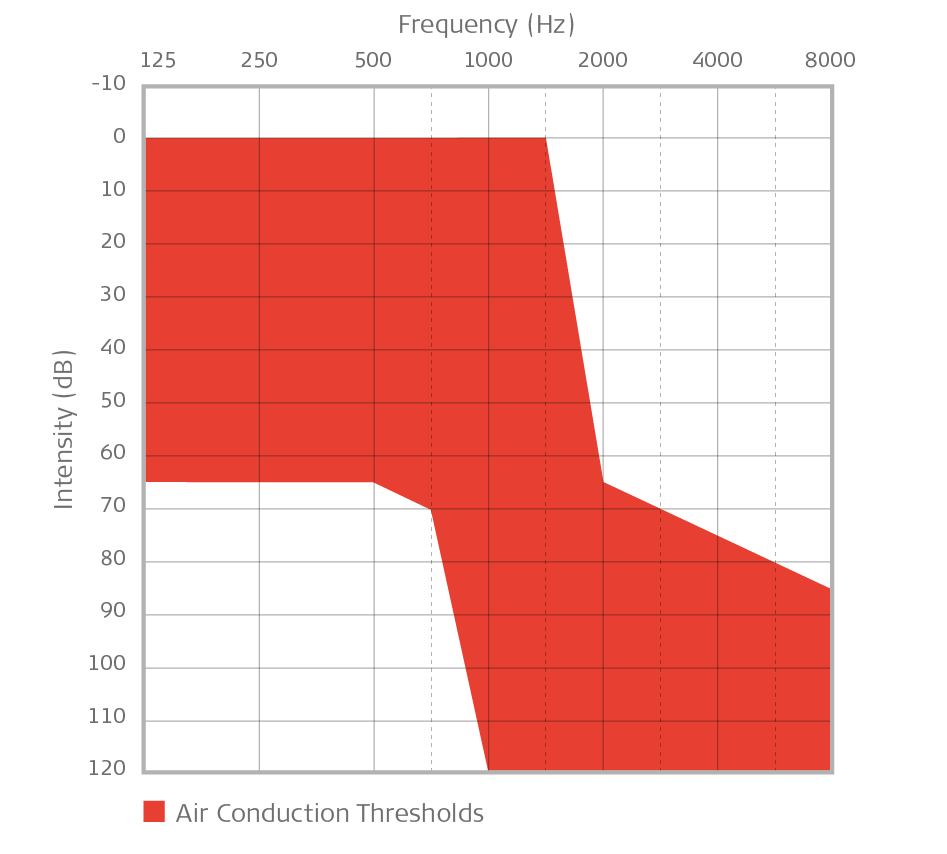
Severe hearing loss: 70 to 90 dB higher than normal. Profound loss: 90 dB or more. The graph to the left represents a blank audiogram illustrates the degrees of hearing loss listed above. Frequency is plotted at the top of the graph, ranging from low frequencies (250 Hz) on the left to high frequencies (8000 Hz) on the right.
Researchers gained insights into how cells in the auditory system become organized to hear different frequencies. The findings could lead to new approaches for certain kinds of hearing loss. The human ear can detect a wide range of frequencies, from the low rumbles of distant thunder to the high-pitched whine of a mosquito.
Nov 01, 2017 · High frequency hearing loss leads to an individual having trouble hearing sounds in the 2,000 to 8,000 Hz range. This means they have trouble hearing the voices of women and young children as well as s, h or f sounds. Sound travels in waves and is measured in frequency and amplitude. Amplitude is the measurement of how forceful a wave is.

Testosterone...A testicular action was linked to circulating blood fractions – now understood to be a family of androgenic hormones – in the early work on castration and testicular transplantation in fowl
People with high frequency hearing loss struggle to hear women's and children's voices clearly because of the higher pitch. Higher pitched sounds usually occur in the 2,000 to 8,000 hertz area of the human hearing range.
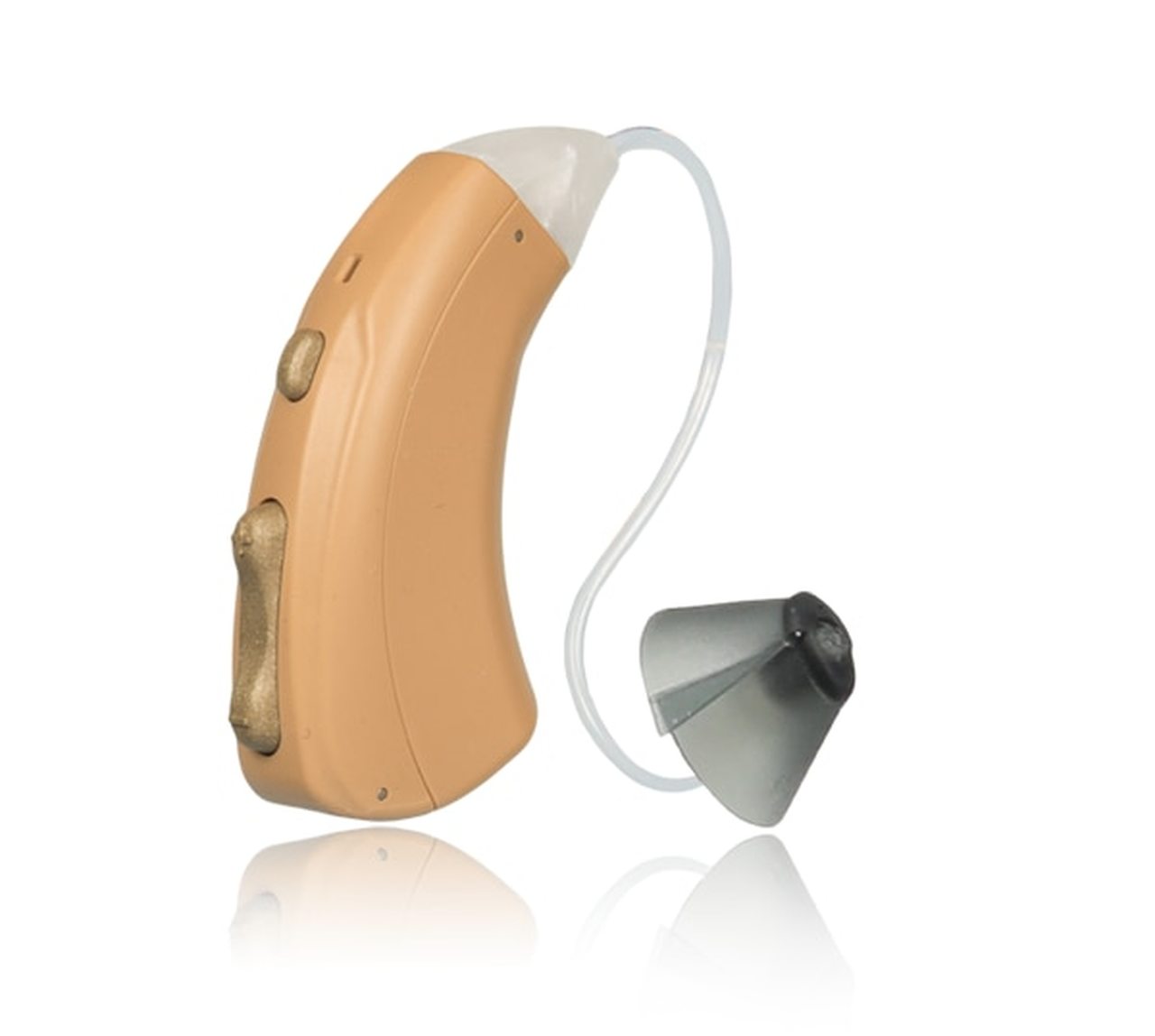
Open-fit hearing aids leave your ear canal at least partially open and are now state-of-the-art for high-frequency hearing loss. Open-fit hearing aids allow low-frequency and mid-frequency sounds into the ear normally, so that only high-frequency sounds are amplified.
High-frequency hearing loss is the result of damage of the sensory hearing cells in the inner ear or cochlea. (This type of hearing loss is also known as "sensorineural hearing loss".) Tiny hair cells in the cochlea serve to render sound from the outside world into electrical impulses that our brains can then recognize as understandable sounds.
High-frequency hearing loss can be caused by a variety of reasons. These include noise, aging, genetics, and disease. Menieres disease affects the inner ear and often happens to people between the ages of 30 and 50 years old. This can cause tinnitus, vertigo, hearing loss, and intense episodic dizziness.
People with high-frequency hearing loss tend to have difficulty hearing certain consonants, like s, h and f. This is because consonants are uttered at a higher frequency than vowels sounds. This can result in speech sounding muffled, especially when talking on the phone, watching TV or trying to have a conversation in background noise.
Neural- downsloping high-frequency hearing loss with a disproportionate loss of speech perception - degeneration of spiral ganglion cells Strial/metabolic- a flat SNHL with preserved speech perception - degeneration of stria vascularis Cochlear conductive- progressive downsloping high-frequency SNHL - increased stiffness of the basilar membrane
What is High Frequency Hearing Loss? High frequency hearing loss refers to having trouble hearing sounds in the 2,000 to 8,000 Hertz (Hz) range. This happens when sensory hearing cells within your ear's cochlea are damaged or die. These hair cells are charged with creating electrical impulses from the sounds that are collected by your ears.

Out-of-body experience...How to Have an Out of Body Experience...Theo's depiction of the separation stage of an out-of-body experience, which often precedes free movement






















0 Response to "42 higher frequency hearing loss"
Post a Comment